You'll be presented with several different solutions.
We recommend following the solutions one by one and checking your microphone after each one to check if the problem is gone. If you think you know what the problem is, though, you can jump directly to the corresponding solution.
Solutions 1-3 are basic checks and configurations everyone should make sure they’ve done.
If you’re planning to get new wired headphones/headset or if you think you might be having a hardware issue, solution 4 would walk you through the hardware basics that you need in order to avoid common compatibility issues.
If you’re using a Bluetooth recording device then all the solutions will be helpful, but pay extra attention to solution 5.
Solutions 6-9 will help you fix your audio drivers and give you some other general tips that could tip the scales in favor of your microphone actually doing its job.
Solution 1: Set correct microphone access permissions
Solution 2: Set default recording device
Solution 3: Disable app-exclusive control
Solution 4: Make sure your hardware is compatible with the mic
Solution 5: Connect your Bluetooth headset manually
Solution 6: Install the right audio driver for your computer
Solution 7: Uninstall the microphone if it exists in the Devices and Printers section
Solution 1: Set correct microphone access permissions
Open Windows' Settings from the start menu.
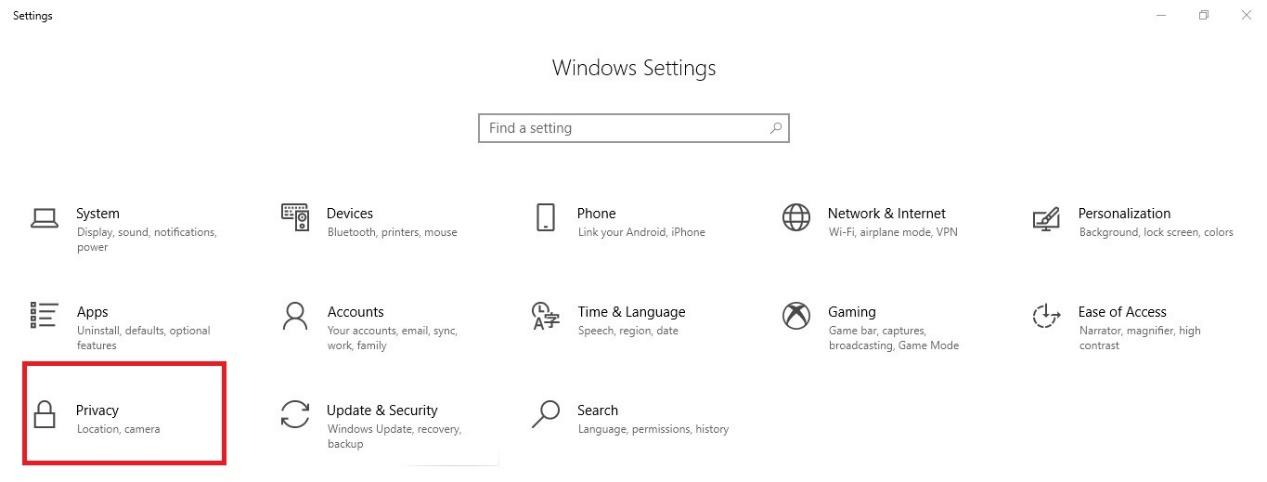
Click the Privacy icon.
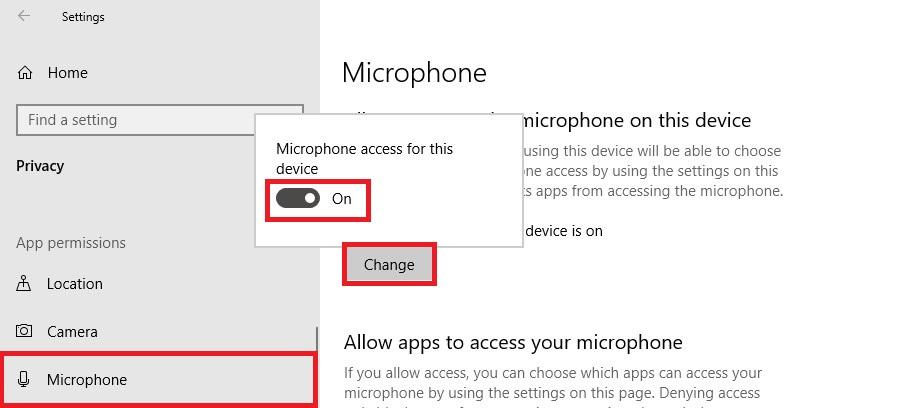
Now from the left pane, select Microphone and then check these three settings:
- If you see “Microphone access for this device is off”, then click the Change button and then turn on “Microsoft access for this device”.
- If your “Allow apps to access your microphone” is Off, please toggle it to On.
- Check the apps list and make sure to enable access for the ones that you’re trying to use.
Solution 2: Set default recording device
Press the Windows logo key + R in order to launch Run.
Type Control Panel and then press Enter or click Ok.
Click Hardware and Sound.
Now click on Sound.
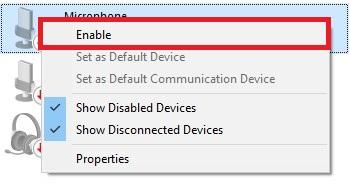
You can see the list of your recording devices in the “Recording” tab, right-click in an empty area in the list and check both Show Disabled Devices and Show Disconnected Devices.
Right-click on each of your recording devices and make sure they are all Enabled (if a device is already enabled, you will see the Disable option in the menu).
Now speak into your microphone. Make sure that you’re away from any other microphones in order to avoid any confusions in the next step.
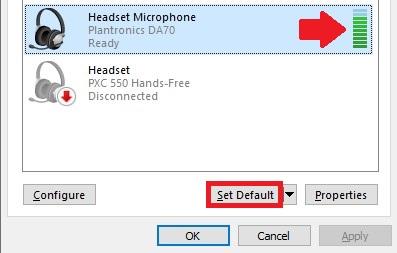
While speaking into the microphone see if you can notice any green bars rising on the screen. If you do see the green bars rising next to a certain device then that is the one you’re looking for. Select it and click the Set Default button.
Note that this button will be greyed out if you have only one device in the list, or if the device is already set as the default one.
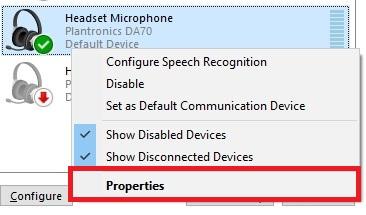
Solution 3: Disable app-exclusive control
Select the microphone from your recording devices list and then click Properties.
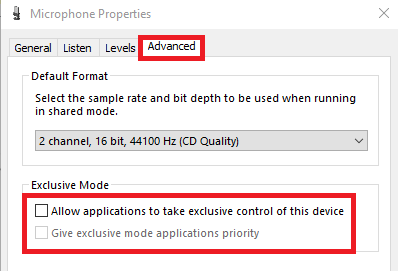
In the Advanced tab, uncheck both options: “Allow applications to take exclusive control of this device” and “Give exclusive mode applications priority”.
Solution 4: Make sure your hardware is compatible with the mic
- A headset with 2 separate 3.5mm jacks: one for the microphone, one for the audio.
- A headset or earphones with only one jack: 2 in 1 (microphone and audio in the same 3.5mm jack)
- A USB headset/headphones with a microphone.
- A Bluetooth headset/headphones with a microphone.
The first two types are a little tricky. Read on.
If your headset/headphones has two separate 3.5mm jacks then your computer/laptop should also have two separate 3.5mm ports (usually one green and one red): one for audio and the other for the microphone. One jack will not suffice.
If you only have one jack on the computer you will need to either get a one-jack headset or a converter that changes from double 3.5mm jacks to a single 3.5mm jack.
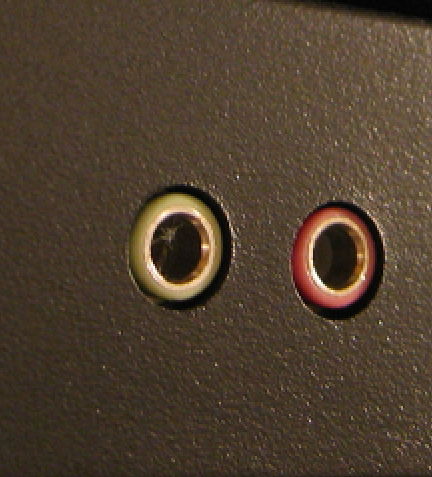
If your headset/headphones has only one 3.5mm jack for both audio and microphone, your laptop should also have one 3.5mm headset port in order to capture both audio and sound from the microphone. A popular example for that is the headphones that come with the old iPhones.

- A single 3.5mm to a double 3.5mm convertor (this one is for single jack headsets in order to connect them to a laptop with dual audio ports)
- A single 3.5mm to USB convertor
- A double 3.5mm to USB convertor
Solution 5: Connect your Bluetooth headset manually
If your headset is connected but no audio comes out of the headset, you have three options:
You can click on the speaker icon, then the little arrow to switch back to the computer/laptop speaker, then switch back again to the Bluetooth headset. Make sure you select the (hands-free or headset) option and not the (Stereo) in order to make the microphone work properly.
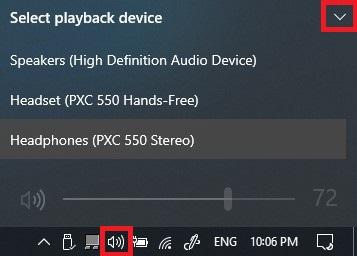
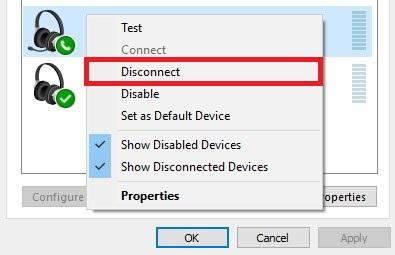
You can go to Control Panel > Hardware and Sound > Sound where you can find the headset listed in the recording devices tab. Right-click on it and choose to Disconnect and then right-click again and choose Connect. This should reset the connection and fix possible mis-connections.
You can always disable Bluetooth and then re-enable it and see if that takes care of the problem.
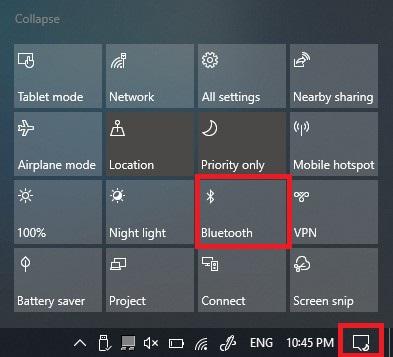
If the Bluetooth headset isn’t already connected, you may want to uninstall the device, put the headset into pairing mode and re-pair it. In order to uninstall the device temporarily, go to Settings > Devices > Bluetooth & other devices and then select the headset and choose Remove Device.
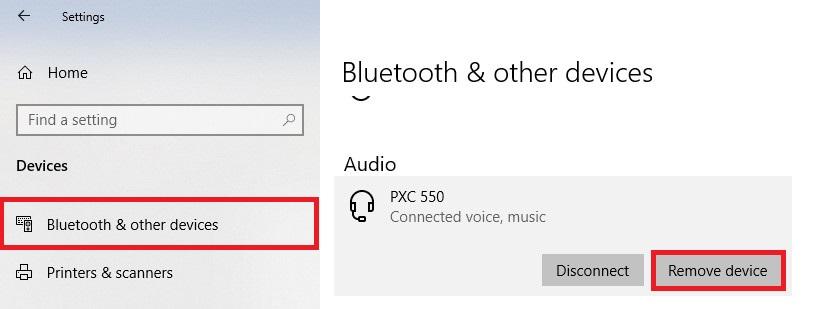
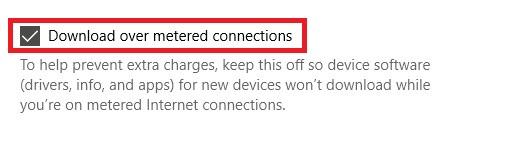
Also, make sure to check the option at the bottom of the same page in order to download the necessary Bluetooth drivers even when you have metered connections. No need to worry about it, it’s usually a small-sized download.
Solution 6: Install the right audio driver for your computer
If for any reason it’s hard to get the official driver and the one you have installed isn’t working correctly, please follow these steps in order to adjust the default driver:
First, disconnect any other connected device as much as you can and leave only your microphone or headset connected.
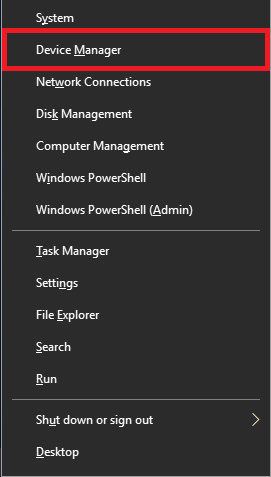
Right-click on your Start button or press Windows logo key + X and select Device Manager.
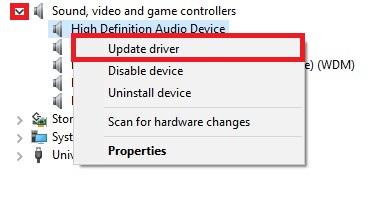
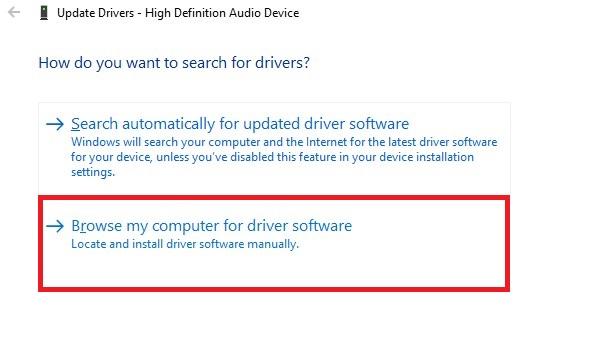
Expand Sound, video and game controllers, right-click on High Definition Audio Device and select Update driver.
Select the second option: Browse my computer for driver software.
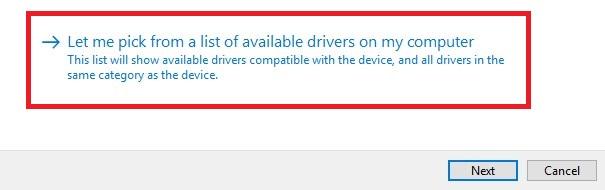
Click this option at the bottom: Let me pick from a list of available drivers on my computer.
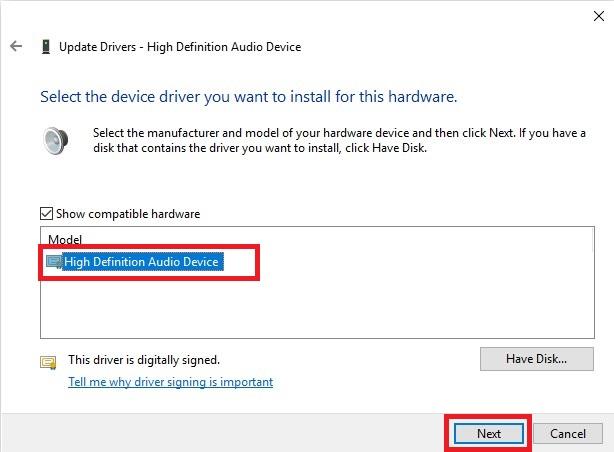
Select High definition Audio Device and then click Next.
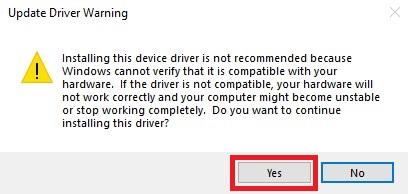
A warning will pop-up confirming that you are making a change to this driver, please click Yes.
Solution 7: Uninstall the microphone if it exists in the Devices and Printers section
If that’s the case, you can always remove the device, unplug or disconnect it and then reconnect it - which would reinstall it and sometimes solve the problem.
Press the Windows logo key + R in order to launch Run.
Type Control Panel and then press Enter.

Click View devices and printers in order to see your devices’ list.
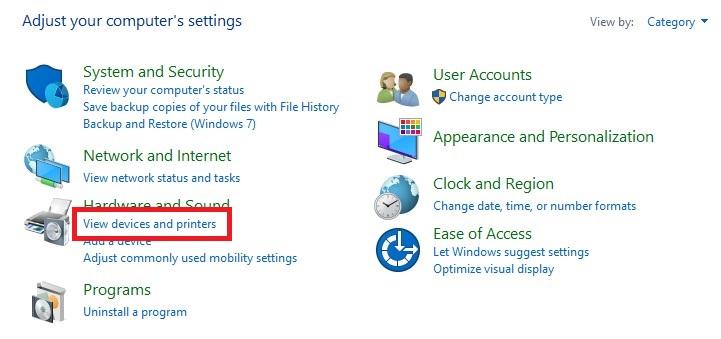
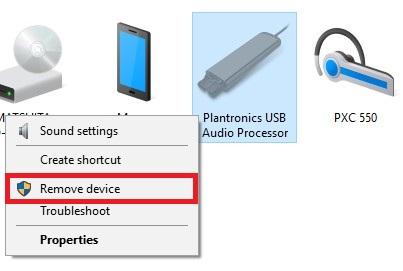
Right-click on the headset, microphone or USB dongle attached to your microphone and click Remove device.
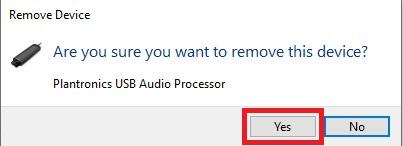
Click Yes in order to uninstall the device.
Solution 8: Uninstall suspicious VOIP apps
Sometimes even if you prevent exclusive control of apps (see solution 3), some VOIP programs like Skype, Zoom, Viber, TeamSpeak, etc. can play with your microphone settings on their own accord and prevent it from working properly.
That’s why it’s recommended that you review your installed voice applications and uninstall the ones that may cause such a problem, including the pre-installed Skype if you don’t really use it.
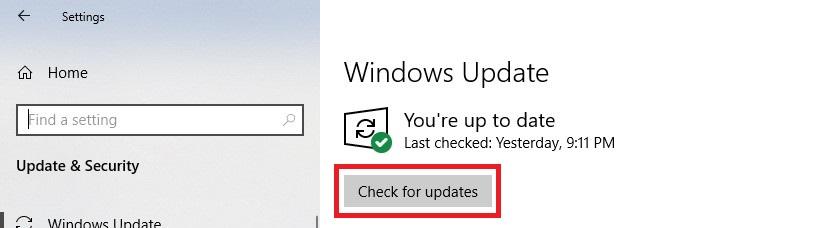
Solution 9: Perform Windows Update
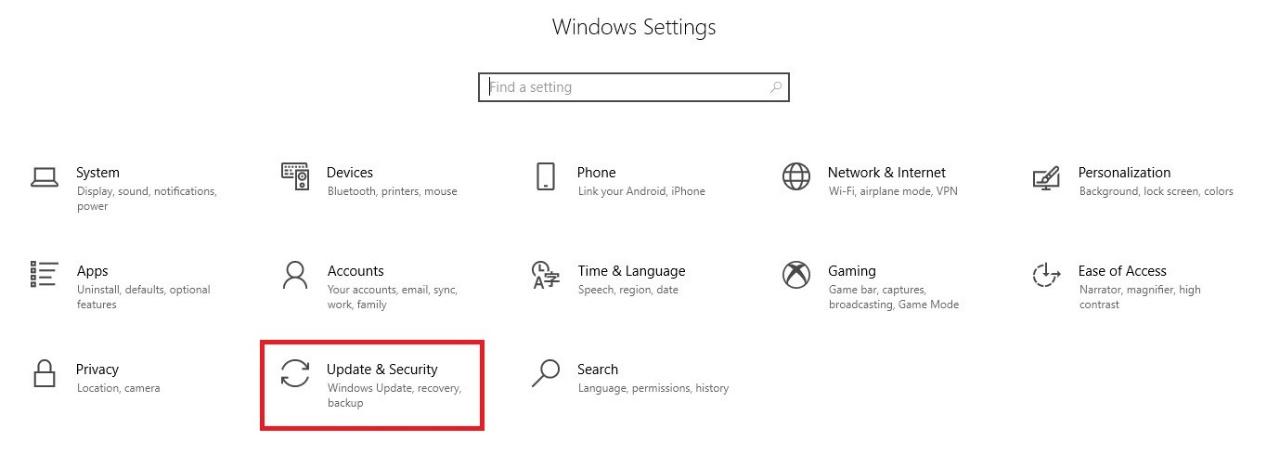
Open Windows' Settings from the start menu.

Click the Update & Security icon.
Click the Check for updates button. If there is an update, make sure it is downloaded and installed.